When trying to conceive, many women come across the term AMH during fertility check-ups. Doctors often mention it when assessing ovarian reserve or planning assisted reproductive treatments. But what does it actually mean, and more importantly—what is a good AMH level to get pregnant? Let’s break it down in detail.
Also read: Uses, Benefits, and Risks of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
What Is AMH?
AMH stands for Anti-Müllerian Hormone, a protein hormone produced by cells in the ovarian follicles. It acts as a marker of a woman’s ovarian reserve, which simply refers to the number of eggs remaining in the ovaries.
Unlike hormones that fluctuate during the menstrual cycle (such as FSH, LH, or estrogen), AMH remains relatively stable throughout the month. This makes it a reliable indicator for fertility specialists to assess a woman’s reproductive potential.
In simpler words: the higher your AMH (within a healthy range), the better your ovarian reserve is likely to be.
How Is AMH Testing Conducted?
Testing for AMH is simple and straightforward:
- Blood Test – A small blood sample is taken at any time during your cycle, since AMH doesn’t fluctuate daily.
- Results Timeline – Reports usually come back within a few days.
- Interpretation – The results help doctors determine fertility potential and whether interventions like IVF may be useful.
Unlike other fertility tests, there’s no need for fasting or cycle-day restrictions, which makes AMH testing very convenient.
Importance of AMH Testing
Why do doctors recommend AMH testing?
- Predicting Fertility Window – It gives an idea of how many eggs a woman might have left.
- IVF Planning – Helps in deciding the right medication doses for ovarian stimulation.
- Assessing Early Menopause Risk – Low AMH can signal premature ovarian aging.
- Understanding Egg Freezing Potential – Women considering fertility preservation often get tested.
While AMH is not a guarantee of pregnancy, it provides valuable insight into reproductive health.
Significance of AMH Levels in IVF
For women undergoing IVF (In Vitro Fertilization), AMH levels are crucial.
- Higher AMH Levels: Suggest more eggs can be retrieved during stimulation.
- Low AMH Levels: May indicate fewer eggs available, making IVF more challenging.
However, it’s important to note that egg quality matters as much as quantity. Even with a low AMH, many women conceive successfully with IVF or natural conception.
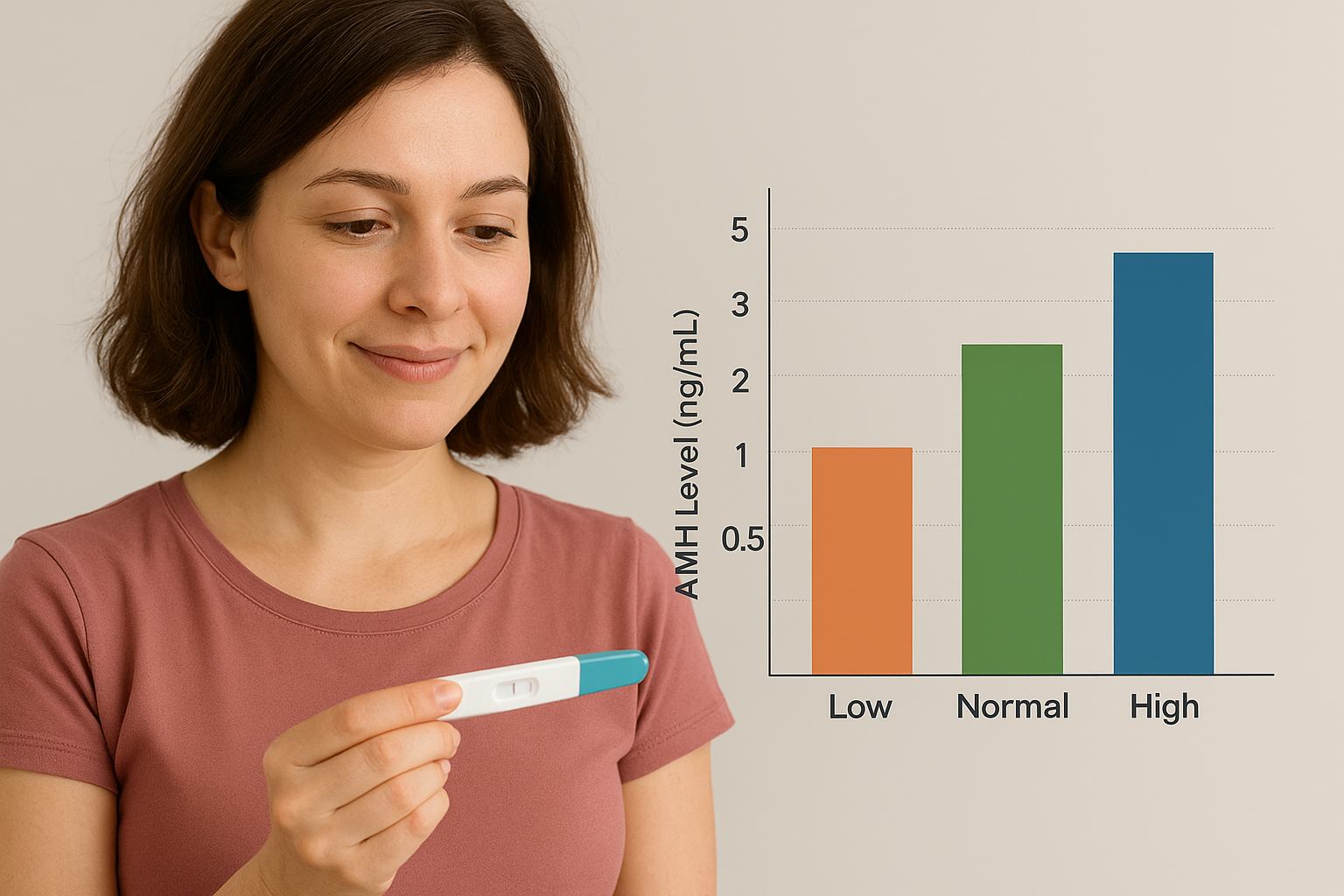
What Are the Normal AMH Levels?
AMH levels are measured in ng/mL (nanograms per milliliter), though the exact reference ranges can vary by lab.
Here’s a commonly used guideline:
- High AMH (>4.0 ng/mL) – May suggest polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or a large egg supply.
- Normal AMH (1.0 – 4.0 ng/mL) – Generally indicates a healthy ovarian reserve.
- Low AMH (0.5 – 1.0 ng/mL) – Signals a reduced egg supply.
- Very Low AMH (<0.5 ng/mL) – Suggests a very limited ovarian reserve.
AMH Levels and Pregnancy
A common misconception is that AMH directly determines whether you can get pregnant. That’s not entirely true.
- Low AMH means fewer eggs are available, but it only takes one healthy egg to conceive.
- High AMH may reflect good egg count but can sometimes signal PCOS, which complicates ovulation.
So, while AMH is an important fertility marker, it’s not the only factor. Age, egg quality, sperm health, uterine condition, and overall health also play critical roles.
Is High AMH a Good Thing?
Many women assume that higher is always better, but that’s not necessarily the case.
- Advantages of High AMH: More eggs in reserve, better response to IVF stimulation.
- Concerns with High AMH: Very high levels may suggest PCOS, which can cause irregular cycles, anovulation, or fertility challenges.
In short, moderately good AMH levels are ideal. Too low or too high both come with challenges.
What Is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant?
This is the big question most women ask.
- A good AMH level for pregnancy is typically between 1.0 – 4.0 ng/mL.
- Within this range, women usually have enough ovarian reserve to conceive naturally or respond well to fertility treatments.
- If AMH is below 1.0 ng/mL, pregnancy is still possible, but conception rates may be lower.
- Women with very high AMH (>4.0 ng/mL) can still conceive but may need help managing PCOS-related issues.
So, the answer is: a balanced AMH level—neither too low nor excessively high—is considered optimal for pregnancy.
Low AMH Levels
Hearing that you have low AMH can feel discouraging, but it doesn’t mean the end of your fertility journey.
- Many women with low AMH still conceive naturally.
- Treatments such as IVF with tailored protocols, egg freezing, or donor eggs remain options.
- Doctors often recommend acting sooner rather than later, as fertility declines with age.
Reasons for Low AMH Levels
Low AMH can result from several factors:
- Age – AMH naturally declines after age 30 and drops more sharply after 35.
- Genetics – Some women are genetically predisposed to early ovarian aging.
- Lifestyle Factors – Smoking, poor diet, and chronic stress may impact egg reserve.
- Medical Conditions – Endometriosis, autoimmune issues, or previous ovarian surgery can reduce AMH.
- Chemotherapy or Radiation – These treatments can significantly impact ovarian reserve.
Lifestyle Tips to Maintain Good AMH Levels to Get Pregnant
While you cannot increase the number of eggs you were born with, you can protect and maintain egg quality through lifestyle choices:
- Balanced Diet – Eat nutrient-rich foods, especially those with antioxidants (leafy greens, berries, nuts).
- Avoid Smoking & Excessive Alcohol – Both are proven to reduce ovarian reserve.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight – Both underweight and overweight can affect hormones.
- Manage Stress – Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance.
- Limit Toxins – Reduce exposure to environmental chemicals like BPA and pesticides.
- Supplements – Coenzyme Q10, Vitamin D, and Omega-3s may support egg health (consult your doctor before use).
These steps won’t magically raise AMH but can optimize your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Also read: Symptoms and Causes of High Cortisol Levels
Conclusion
As we discussed in above article that what is a good amh level to get pregnant. AMH is a valuable tool for understanding fertility potential, but it’s not the ultimate predictor of pregnancy. A good AMH level to get pregnant usually falls between 1.0 – 4.0 ng/mL, though many women conceive outside this range.
Whether your AMH is low or high, remember: age, egg quality, lifestyle, and medical support play equally important roles in conception. If you’re concerned about your fertility, consulting a reproductive endocrinologist is the best step forward.
FAQs About AMH and Pregnancy
1. Can you get pregnant with low AMH?
Yes, many women with low AMH conceive naturally. However, success rates may be lower, and early medical support may be helpful.
2. Does AMH affect egg quality?
No, AMH reflects egg quantity, not quality. Egg quality is mostly determined by age.
3. Can high AMH cause infertility?
Not directly, but high AMH is often linked with PCOS, which can cause irregular ovulation and make conception harder.
4. At what age should I test my AMH?
Women in their late 20s or early 30s who are curious about fertility, or those struggling to conceive, may benefit from testing.
5. Can lifestyle changes improve AMH?
Lifestyle changes don’t increase AMH but can improve egg health and overall fertility potential.