In the evolving landscape of women’s healthcare, knowledge serves as the ultimate source of empowerment. Making informed decisions about your body requires an understanding of available options, the latest medical advancements, and the long-term implications of each choice. One procedure that has gained prominence for its dual role in cancer prevention and permanent contraception is the salpingectomy.
This comprehensive guide aims to clarify the surgical intervention of salpingectomy, exploring what it entails, the specifics of a bilateral salpingectomy, the minimally invasive approach of a laparoscopic salpingectomy, and the significant impact it can have on your health journey. Our goal is to provide you with detailed and accurate information, enabling you to engage confidently with your healthcare provider and feel empowered to take charge of your well-being.
What is Salpingectomy?
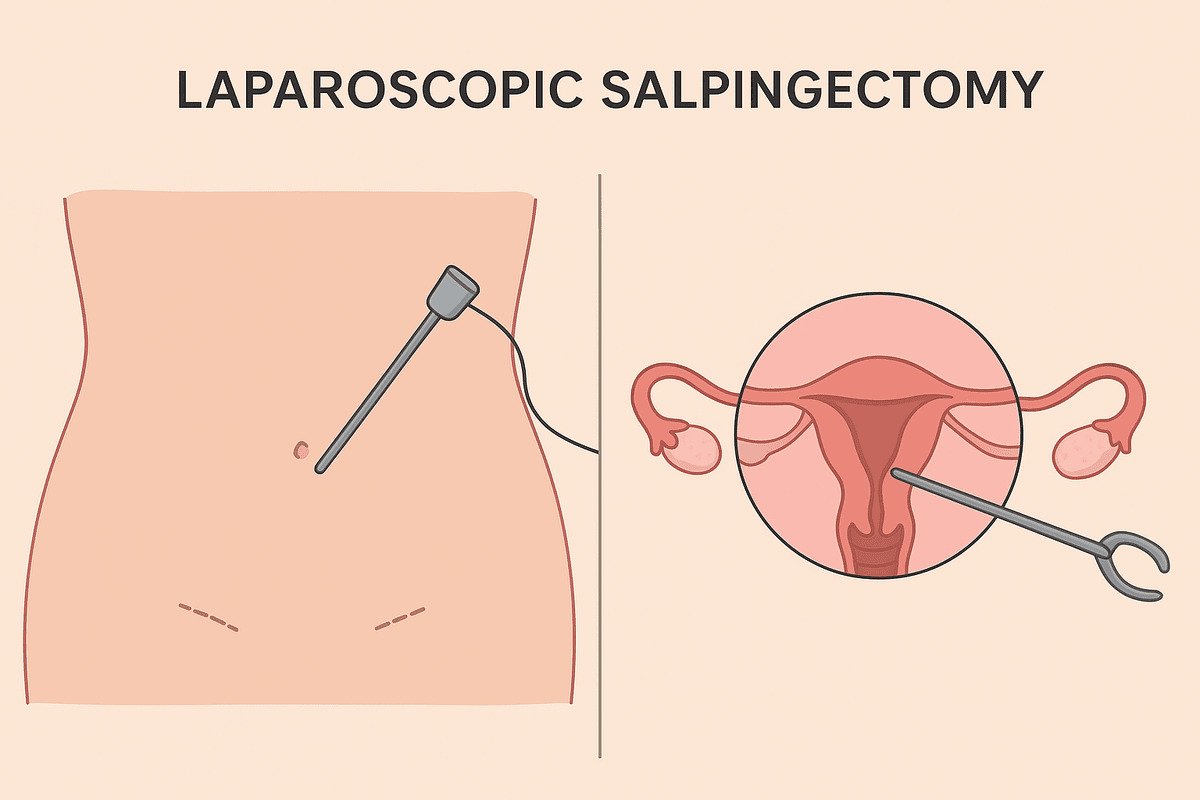
A salpingectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one or both fallopian tubes. These slender, muscular structures connect a woman’s ovaries to her uterus and serve as the pathway for an egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus each month. Fertilization by sperm typically occurs within these tubes. The term “salpingectomy” is derived from the Greek words “salpinx,” meaning trumpet (referring to the tube’s shape), and “ektomē,” meaning excision.
Understanding this procedure begins with recognizing the two primary types: a unilateral salpingectomy, which involves the removal of one fallopian tube, and a bilateral salpingectomy, which consists of the removal of both tubes. We will explore the varying reasons for choosing one option over the other, which typically depend on specific medical circumstances or personal health goals, in greater detail throughout this article.
Why Choose a Salpingectomy?
The decision to undergo a salpingectomy is significant and based on various compelling medical reasons, ranging from treatment to proactive prevention. Historically, fallopian tube removal was most often performed to address immediate health issues such as ectopic pregnancy. In this condition, a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterine cavity, most commonly within a fallopian tube, creating a life-threatening situation that requires urgent surgical intervention.
Other traditional reasons for salpingectomy include treating infections like severe pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) that damage the tubes, addressing blockages or hydrosalpinx (a fluid-filled tube), and removing benign growths or cysts. However, recent discoveries in gynecologic oncology have revolutionized the role of salpingectomy as a premier preventive measure in healthcare.
The Ovarian Cancer Prevention Breakthrough
In recent years, extensive research has revealed that the most common and aggressive type of ovarian cancer, high-grade serous carcinoma, actually originates not in the ovaries but in the fimbriated ends of the fallopian tubes. This groundbreaking discovery has established the bilateral salpingectomy as a powerful preventive tool. For women undergoing pelvic surgery for reasons such as hysterectomy or permanent birth control, opting to remove the fallopian tubes can significantly reduce their lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer. This opportunistic salpingectomy empowers women to drastically lower their risk of a cancer that is notoriously difficult to detect in its early and most treatable stages.
Salpingectomy as a Form of Permanent Birth Control
For women who have completed their families and seek permanent fertility cessation, a bilateral salpingectomy has quickly become the new gold standard. This method surpasses the traditional tubal ligation, often referred to as “having your tubes tied.” While tubal ligation involves cutting, clamping, or sealing the tubes to block them, a bilateral salpingectomy entails their complete removal. This approach is more effective at preventing pregnancy and offers the added benefit of reducing ovarian cancer risk. Eliminating the tubes virtually eliminates the chance of tubal ligation failure from recanalization or the tubes reconnecting, providing unmatched peace of mind.
The Specifics of a Bilateral Salpingectomy
A bilateral salpingectomy involves the complete removal of both the left and right fallopian tubes. This procedure is frequently discussed in relation to both permanent contraception and cancer risk reduction. It is definitive, rendering natural conception impossible since there is no longer a pathway for the egg to meet the sperm. Importantly, this procedure does not involve the ovaries. The ovaries remain intact and continue to function normally, producing eggs and secreting hormones like estrogen and progesterone. As a result, women who undergo a bilateral salpingectomy will not experience surgical menopause; their menstrual cycles will persist until they reach natural menopause age. This distinction is crucial for women who are concerned about hormonal changes after surgery because it preserves ovarian function and maintains the body’s natural endocrine balance.
This proactive step not only provides effective birth control but also plays a vital role in reducing the risk of ovarian cancer, making it a significant choice for women’s health.
Unveiling Laparoscopic Salpingectomy
When performing a salpingectomy, the chosen surgical technique has a significant impact on recovery and scarring. Today, most planned salpingectomy procedures utilize minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques. A laparoscopic salpingectomy is a remarkable advancement in modern surgery. It involves the removal of the fallopian tubes through several small incisions, typically measuring 0.5 to 1 cm each, in the abdomen. The surgeon inserts a laparoscope, a thin, lighted tube equipped with a high-resolution camera, through one incision. This device projects a magnified view of the internal organs onto a monitor. The surgeon then introduces specialized surgical instruments through the other tiny incisions to carefully dissect and remove the fallopian tubes. This method contrasts sharply with traditional open surgery (laparotomy), which requires a much larger incision.
Advantages of a Laparoscopic Bilateral Salpingectomy
Choosing a laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy offers numerous advantages that enhance the patient experience. These benefits include a significantly lower risk of infection due to smaller incisions, reduced post-operative pain, and a much shorter recovery time. Many women can return to work and normal activities within one to two weeks. The procedure also results in minimal and cosmetically pleasing scarring and decreased blood loss during surgery.
The precision provided by the laparoscopic camera enables surgeons to obtain an excellent view of the pelvic anatomy, facilitating a meticulous and safe operation. In more complex cases, such as those involving extensive scar tissue from previous surgeries or endometriosis, the surgeon may employ a robotic-assisted laparoscopic approach to enhance their dexterity and visualization.
Factors Influencing Your Chances of IVF Success with Own Eggs
The Salpingectomy Journey from Consultation to Recovery
The journey toward a salpingectomy begins with a comprehensive consultation with your gynecologist or gynecologic surgeon. This discussion is crucial for informed decision-making. During this meeting, you should expect to review your complete medical and surgical history, motivations for seeking the procedure (such as contraception or cancer risk reduction), and all available alternatives. Your surgeon will explain the procedure in detail, including its risks, benefits, and what to expect during recovery. It is essential to ask any questions you may have during this consultation; no question is too small. Remember, this is about your health.
The Recovery Process After a Laparoscopic Salpingectomy
Understanding the typical recovery timeline after a laparoscopic salpingectomy helps set realistic expectations and promotes smoother healing. Recovery experiences vary, but most women can go home on the same day as their surgery or after an overnight hospital stay. You may experience some abdominal soreness, shoulder tip pain (from gas used to inflate the abdomen during laparoscopy), and general fatigue for the first few days. You can often manage these symptoms with prescribed or over-the-counter pain medications. Your care team will advise you to rest for about a week and to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise. However, short walks are encouraged to promote circulation and healing. Many women can return to desk work within a few days to a week; full resumption of all activities, including intense workouts, may take up to four weeks. Your surgeon will provide personalized instructions for your post-operative care.
Weighing the Considerations: Risks, Efficacy, and Hormonal Impact
As with any surgical procedure, it is vital to understand the potential risks associated with a salpingectomy. While major complications are rare in laparoscopic procedures, they can include reactions to anesthesia, bleeding, infection, and injury to nearby organs such as the bladder or intestines.If unexpected challenges arise, the surgical team may convert the procedure from laparoscopy to an open laparotomy. We consider a bilateral salpingectomy to be over 99% effective, ranking it as one of the most reliable birth control options available. Significantly, the procedure does not induce menopause. Since the ovaries remain intact and continue to receive a blood supply, they produce hormones as they usually should. Thus, your body’s natural hormonal cycle continues uninterrupted.
Salpingectomy vs. Other Procedures
To make an informed decision, it is helpful to compare a salpingectomy with other similar procedures. The most common comparison is with tubal ligation. Both methods are permanent; however, salpingectomy offers superior effectiveness and reduces the risk of cancer. Another procedure for comparison is a hysterectomy, the removal of the uterus. This procedure ends menstruation and eliminates the ability to carry a pregnancy, but it does not significantly lower ovarian cancer risk unless the surgeon also performs a bilateral salpingectomy. It is also distinct from oophorectomy, which involves removing the ovaries and leads to immediate surgical menopause. Medical guidelines typically recommend oophorectomy only for women at very high genetic risk for ovarian cancer.
Also Read: ICSI vs Conventional IVF: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Empowerment Through Knowledge: Your Questions Answered
Will my periods change after a salpingectomy?
No, your periods will not change. Since your ovaries remain intact, your hormonal cycle continues as before. You will still ovulate, but the egg will be absorbed by your body rather than traveling down the fallopian tube. Therefore, you will continue to have regular menstrual periods.
Is salpingectomy reversible?
No, a bilateral salpingectomy is designed to be a permanent procedure. Because the entire fallopian tube is removed, it cannot be surgically reversed. If you may want to become pregnant in the future, consider exploring reversible contraceptive options instead.
Does insurance cover this procedure?
Most insurance plans cover a salpingectomy when deemed medically necessary, including its use for permanent contraception. However, coverage can vary by plan. It is essential to contact your insurance provider before the procedure to understand your specific benefits, copays, and any prior authorization requirements.
Embryo Transfer Hydration Secrets
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Reproductive Health
Deciding to undergo a salpingectomy is a significant and personal choice that involves family planning, cancer prevention, and overall health strategy. The advancement of laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy marks a success in minimally invasive surgery. This procedure offers a safe, efficient option with a quick recovery time and lasting benefits. By choosing to remove the fallopian tubes, women select an effective method of permanent birth control while proactively reducing their risk of certain cancers.
With this knowledge, you are better equipped to engage in meaningful discussions with your healthcare provider. Remember, the most empowered patient is one who is informed. Reflect on your personal health goals and take the next step toward owning your health narrative with confidence and clarity.